Thoracic osteochondrosis is a chronic process of degenerative dystrophy that causes damage to the intervertebral discs and vertebral bodies of the thoracic spine. This disease is less common than spine osteochondrosis of the neck or waist. However, this does not mean that it will not cause trouble to people. Thoracic osteochondrosis mainly manifests as back and chest pain, but it may also cause heart and abdominal pain, similar to angina or liver colic. In rare cases, thoracic osteochondrosis becomes the cause of the development of lower limb muscle paralysis, their sensitivity is impaired, and pelvic organ diseases. The treatment of the disease consists in the use of drugs and non-drug methods, and sometimes even surgery. From this article, you will learn about the symptoms and treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis.
Thoracic spine
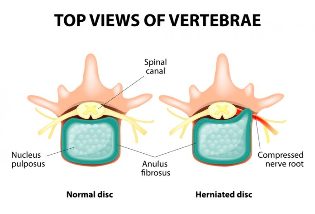
The thoracic spine is represented by 12 vertebrae with intervertebral discs between them. The intervertebral disc is composed of nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus. The pathological changes of these intervertebral discs and adjacent facet joints, the growth of bone spurs along the edges of the vertebral body, the malnutrition process of the spinal ligaments, and the direct cause of back pain.
It should be understood that osteochondrosis, as a disease, rarely affects only part of the spine. Usually, this process is diffuse, more or less obvious in various parts of the spine.
Certain structural features of the thoracic spine make it less affected by osteochondrosis than other spine areas. Let's list these features:
- Lower thoracic spine mobility;
- The junction of the vertebrae and ribs (combined with the sternum to form a strong chest frame, which is not easy to be injured);
- The thickness of the intervertebral disc is small;
- Physiological kyphosis of the thoracic spine (curved in the front-to-back direction and has a rearward bulge), so the maximum axial load falls on the front of the disc instead of the back.
The development of thoracic osteochondrosis is not another feature of the structure, but the smaller frequency of thoracic spine pain, which also determines that the existing morphological basis of osteochondrosis in this site can be maintained in the clinic for a long time. "status. In other words, there are changes, but they will not bother the patient.
However, in the presence of irritating factors, such as a sedentary lifestyle (including working at a desk or driving a car for many years), injury, poor posture, sagging back muscles, physical labor in a forced posture, thoracic spineOsteomyelia reveals his true colors.
Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis

- reflection;
- Compression.
Reflex syndrome is a clinical manifestation of spinal receptor stimulation. These are the receptors of ligaments, intervertebral joint capsules, and intervertebral discs. They receive pathological impulses in osteochondrosis. In addition to pain, reflex syndrome can also be accompanied by muscle tension and malnutrition of soft tissues and internal organs. This change is based on the fact that the stimulation of the receptor causes the excitement to spread to the structures near the spinal cord (more precisely the various parts of the spinal cord). These may be neurons responsible for perspiration in a certain area of the skin, regulating the temperature of the same area, participating in ensuring the activities of internal organs (heart, liver, intestine, etc. ), and maintaining the tone of the muscles and blood vessels that provide all these structures. When the excitation is delivered to these neurons, there will be corresponding symptoms of interruption of certain morphological activities. Therefore, when the pain in the abdomen or heart area is caused by osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, this situation is entirely possible.
Compression syndrome occurs when the nerve root is compressed (less stretched) when it leaves the intervertebral foramen, spinal cord tissue or blood vessels that feed the nerve. Compression syndrome is almost always caused by an existing disc herniation. The most common is the lower thoracic hernia. Depending on the direction and location of the hernia, a person will experience certain symptoms. It can be expressed as follows:
- The middle (middle) hernia is accompanied by symmetrical muscle weakness and loss of sensitivity in both legs. At the same time, there is no typical pain syndrome of nerve root compression.
- Lateral (lateral) hernia only shows pain related to nerve root compression;
- The mid-lateral hernia combines the clinical symptoms of the first two groups, and only muscle weakness and sensory disturbance are dominant.
Which syndromes are considered in the framework of thoracic osteochondrosis? Let us discuss the types of reflex and compression syndromes at this level in more detail.
Reflex syndrome
Dorsago-Sudden severe pain in the thoracic spine. It has a sharp nature and is usually described by patients as a dagger. Basically, it feels between the shoulders and the bones, which can be applied to the heart, sternum. As this condition exacerbates the pain (as if it is recurring), the patient is afraid to move or even breathe deeply. Usually, when performing monotonous work, similar symptoms will appear after staying in a fixed and uncomfortable posture for a long time. Sudden movements thereafter will arouse back pain in patients with thoracic osteochondrosis. When palpating the thoracic spine, it will show the tension and soreness of the roller-like paraspinal muscles.
Sometimes this pain can be considered a heart attack, so severe and sudden for the patient. However, the ECG collected was not abnormal, and using nitroglycerin under the tongue did not eliminate the pain.
Back painis another reflex chest level syndrome. It is a progressive pain syndrome. The pain can be located on the back, anywhere on the chest. Pain, dull pain, sometimes with a faint burning sensation (related to the stimulation of the plant structure). As the spine moves, bends, rotates around its axis, coughs or sneezes, and drives on rough and uneven roads, it will intensify.
Pain is felt in the intercostal space on one or both sides. This function is attributed to the movement of nerve conductors (intercostal nerves and blood vessels are located in the intercostal space). In this case, similar to shingles pain, this pain is called intercostal neuralgia.
If the pain is on the front chest wall, it is also called chest pain. However, it can only be felt if certain places are intact. For example, in the area of the xiphoid process or the attachment site of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Often, due to the painful and dull nature of the pain, it is difficult to figure out the exact location of the pain: something inside the chest or in the superficial soft tissue area.
The reflex syndrome of thoracic osteochondrosis is more common than compression.
Compression Syndrome
Nerve root compressionThe first is pain syndrome. Pain spreads in nature. The direction of pain propagation corresponds to the progression of nerve fibers. In the case of sternal osteochondrosis, these are intercostal spaces. Because some nerve fibers form nerve plexuses involved in the innervation of internal organs, pain in the chest and abdomen will be felt. Pain increases with exercise, body bending, coughing, sneezing, and laughing (because the root tension increases at this time). In the area innervated by the compressed root, sensitivity disorders can be observed: peristalsis, numbness, tingling. It may not feel good to touch the area. If nerve roots are compressed for a long time, dyskinesias, that is, weakness of the innervated muscles, may occur. The muscles gradually atrophy. However, dyskinesias are very rare because they are the latest in the chronological order of onset of all symptoms. Usually, a person seeks medical help at the stage of pain and sensory disturbance.
Spinal cord compressionIt is manifested as weakness in the legs, accompanied by increased muscle tone (if the spinal cord is compressed in the lower chest spine, muscle tone will decrease). Pathological foot symptoms may appear (Babinsky, etc. ). The sensitivity of the lower limbs is lost, and the sensation of hot and cold contact is no different, just the difference between contact and injection. In the case of severe compression of the spinal cord, urinary system diseases may occur.
Compression of the blood vessels supplying the spinal cordleads to the development of bone marrow ischemia, that is, malnutrition of spinal cord tissue. This condition and the compression of the spinal cord are accompanied by the development of muscle weakness (patients say "the legs have failed"), loss of sensation and pelvic disease.
It can be said that compression of the spinal cord and its blood vessels is very, very rare in thoracic osteochondrosis.
Nutritional components of thoracic osteochondrosis

Since the nerve fibers from the thoracic spine contain autonomic nerves, the stimulation or damage of these nerve fibers may be accompanied by autonomic symptoms. These can be:
- Dry and peeling skin in another innervated area;
- Local violation of sweating and thermoregulation (also depends on the innervation area);
- Cold lower limbs, weak toenails;
- Simulate the pain of gastrointestinal diseases (such as gastritis, gastric ulcer, cholecystitis, etc. ); Kidney pain is actually not related to kidney pathology (there is no change in urine and ultrasound);
- Pain in the heart area is very similar to angina or even myocardial infarction.
The particularity of this pain may be the fact that a person may not feel back pain. When seeking medical help, this initially misleads patients and medical staff. However, many other research methods can rule out the pathology of internal organs, and then it is believed that osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is considered to be the cause of this pain.
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis
Drugs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have been successfully used to eliminate pain syndrome. This group of drugs has the ability to reduce the inflammatory process, eliminate pain and prevent platelet aggregation. The drugs are prescribed for an average of 7-14 days. Usually, this is enough to eliminate pain. Many of them are available in various forms (tablets, capsules, injections, rectal suppositories) to ensure ease of use. On the first day of treatment, the medicine is used in an injectable form and then converted to tablets or suppositories. The same medicine can be used at the same time locally: in the thoracic region. In addition, there are various release forms for this purpose: creams, ointments, gels, plasters.
Sometimes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are not enough to relieve pain. In this case, use a painkiller mixture. The mixture is injected intravenously into saline or glucose.
Paravertebral block has a very good rapid analgesic effect. This is a medical procedure when a medicinal substance is injected into the thickness of the muscle tissue intracutaneously, subcutaneously, around the nerve (directly near the nerve or root). This procedure requires certain skills and experience of the doctor.
Similarly, local irritating and dispersing ointments can be used to relieve the pain of thoracic osteochondrosis. These are ointments containing snake venom, bee venom and pepper extract.
Non-drug methods can relieve muscle tension.
Diuretics, hormones, Escina Lysinat are used to relieve nerve root edema.
Pentoxifylline, Dipyridamole, Complamin, Niacin are used to normalize blood circulation, improve tissue nutrition and restore nutrition.
In thoracic osteochondrosis, B vitamins are shown to have analgesic and neurotrophic effects.
When the deterioration of thoracic osteochondrosis is prevented, you can resort to drugs that improve the metabolism of the intervertebral discs and joints. These are so-called chondroprotective agents. These drugs stimulate the regeneration of articular cartilage and stop the degeneration of the intervertebral disc. They were prescribed for a long time (3-6 months).
Non-drug methods
Including:
- Massage (classic, acupuncture points, reflex segmentation);
- Physiotherapy practice;
- Stretching spasmodic muscles (there are special techniques, stretching is not performed according to the principle of "what you want");
- Acupuncture;
- Swimming (very useful for all patients with osteochondrosis);
- Physiotherapy (ultrasound, electrophoresis, ampoule, radial flow, mud therapy, etc. ).
If a hernia due to thoracic osteochondrosis compresses the spinal cord, its blood vessels or nerve roots, and at the same time causes muscle weakness, pelvic organ dysfunction, obvious pain syndrome (resistance to drug use), it is consideredThis question is about performing surgery.
Thoracic osteochondrosis is not a fatal disease, but it can cause a lot of harm to the patient. It restricted his life, interfered with work and good rest. The main symptom of thoracic osteochondrosis is pain. It is impossible to get rid of this disease completely, but it is possible to stop the degeneration process and minimize its manifestations.





































